Compendium Review #1 Unit 1
Unit 1 Topics and sub topics:
-Basic characteristics of life
-Molecules of life
-Cell structure and function
-Cell organelles and Metabolism
-Tissue types
Basic characteristics of life
Life starts with the atom the smallest unit composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons which make up elements. All things even humans are made up of elements. These elements help keep life in homeostasis, a state of equilibrium. All living things have basic characteristics. Homeostasis is one of them along with consumption of material for energy, reproduction to keep species alive, growth and development, responding to internal and external stimuli, and evolution to keep up with changes in surroundings.
Molecules of Life
All living things are composed of molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen. These molecules are know as organic molecules and in Biology there are “four categories, called carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.” (Mader pg 27) Carbohydrates are a “function for quick and short-term energy storage in all organisms, including humans”. (Mader pg 28) Glucose, a carbohydrate or 6-carbon sugar, is what our body uses as its quick source of energy. Common sources of carbohydrates are starchy foods like potatoes, bread, and cake. When consuming these products glucose enters the blood and is stored in the liver and released periodically to keep “the blood glucose concentration about 0.1%.” (Mader pg 28) High-fiber carbohydrates (beans, fruits, peas, and vegetables) contribute to a healthy diet, its processed and refined grains that need to be avoided. Lipids are all common in the area that they are insoluble in water. Lipids are different from all other molecules in that they contain more energy. Fats and Oils, like shortenings, butter, and processed foods are all types of Lipids. Lipids are determined by there structure. Saturated fats have no double bond between the carbons in the molecule, while unsaturated fats do have a double bond between the carbons.
-Basic characteristics of life
-Molecules of life
-Cell structure and function
-Cell organelles and Metabolism
-Tissue types
Basic characteristics of life
Life starts with the atom the smallest unit composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons which make up elements. All things even humans are made up of elements. These elements help keep life in homeostasis, a state of equilibrium. All living things have basic characteristics. Homeostasis is one of them along with consumption of material for energy, reproduction to keep species alive, growth and development, responding to internal and external stimuli, and evolution to keep up with changes in surroundings.
Molecules of Life
All living things are composed of molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen. These molecules are know as organic molecules and in Biology there are “four categories, called carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.” (Mader pg 27) Carbohydrates are a “function for quick and short-term energy storage in all organisms, including humans”. (Mader pg 28) Glucose, a carbohydrate or 6-carbon sugar, is what our body uses as its quick source of energy. Common sources of carbohydrates are starchy foods like potatoes, bread, and cake. When consuming these products glucose enters the blood and is stored in the liver and released periodically to keep “the blood glucose concentration about 0.1%.” (Mader pg 28) High-fiber carbohydrates (beans, fruits, peas, and vegetables) contribute to a healthy diet, its processed and refined grains that need to be avoided. Lipids are all common in the area that they are insoluble in water. Lipids are different from all other molecules in that they contain more energy. Fats and Oils, like shortenings, butter, and processed foods are all types of Lipids. Lipids are determined by there structure. Saturated fats have no double bond between the carbons in the molecule, while unsaturated fats do have a double bond between the carbons.

Steroids another form of lipids are not structured like fats are instead they have a four carbon rings bonded together. “Each one differs primarily by the functional groups attached to the rings.” (Mader pg 32) Cholesterol, and sex hormones are all types of steroids. Proteins aid in the structure and function of all cells. Structural proteins make up collagen, nails, and support skin. While other types of proteins transport molecules in the blood, prevent antigens from destroying cells, and allow muscles to move contract. DNA and RNA are types of nucleic acids. DNA stores, replicates and transmits the genetic information of an organism ever time a cell duplicates or an organism reproduces. DNA gives instructions “regarding the amino acid sequence in a protein” and RNA carries them through if there is a fault in DNA’s instructions illness can occur. (Mader pg35)

Cell structure and function
A cell has many different parts starting with the outer shell the plasma membrane which protects and regulates molecules from entering and exiting the cell. Within the cell is cytoplasm a semi fluid that contains organelles and where cell functions are completed. There are two kinds of cells prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and are smaller and less complicated than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotic cells and are used in biotechnology products. Eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells and have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells each have their own function in an organism. For example gamete cells also known as egg or sperm cells are for reproduction. Hormone secreting cells like somatotropes produce growth hormones, and white blood cells fight off infections in our bodies.

Prokaryotic cell
Cell Organelles and Metabolism
The cell is composed of many organelles each having there own function. The nucleus is comprised of the nuclear envelope (encloses the nucleus), chromatin (DNA and protein) and nucleolus (produces subunits of ribosomes). Important organelles in the cell are lysosomes that digest cell parts, a vesicle that transports and stores substances, and golgi apparatus that modifies and distributes secretory products.
Mitochondrion an organelle in the cytoplasm performs cellular respiration which coverts energy of glucose into chemical energy of ATP molecules. During this process mitochondria uses up oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. This process of cellular respiration of mitochondrion is very important to cellular metabolism.

Eukaryotic cell
Tissue Types
Tissue is cells of the same type organized together to perform a common function. There are four tissue type connective, muscular, nervous, and epithelial tissues.
Tissue is cells of the same type organized together to perform a common function. There are four tissue type connective, muscular, nervous, and epithelial tissues.
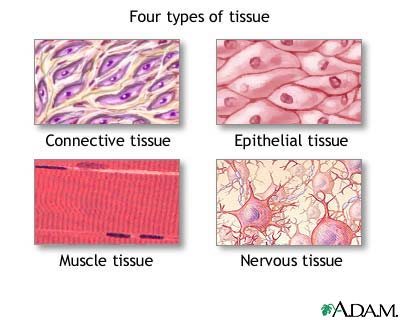
Connective tissue binds and supports other tissues together. There are four kinds of connective tissue fibrous, supportive, and fluid. Loose and dense fibrous tissue is important and present in lungs, arteries and the urinary bladder. Cartilage and bone are types of supportive connective tissue and blood and lymph are types of fluid connective tissue. Connective tissue is made up of ground substance , stem cell, fibroblast and many other characteristic shown in the diagram below.

Muscular tissue is composed of muscle fibers which contain protein filaments and myosin filaments. Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle are the three types of vertebrate muscular tissues. Skeletal muscle is voluntary when it contracts body parts move. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones by tendons. They are cylindrical and long and with multiple nuclei in the striated cells. Smooth or visceral muscle is involuntary with a single nuclei for each spindle-shaped cells. Smooth muscle lines blood vessels and the digestive tract. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart and has characteristics from both smooth and skeletal. Its has branching striated cells like skeletal but with only a single nuclei and it too in involuntary like smooth.

Nervous tissue is made up of neurons and neuroglia and is how the brain knows sensation. “The nervous system has just three functions: sensory, input, integration of data, and motor output.” (Mader pg 66) Neurons are made of three parts the dendrites, cell body, and an axon. Dendrites are the input side they receive messages from other neurons. The cell body houses the nucleus, organelles, and cytoplasm. An axon is the output side using the terminal buttons to send other neurons messages. Neuroglia primary function “is to support and nourish neurons.”(Mader pg66)

Epithelial tissues are cells of uniform type and are joined by a basement membrane composed of carbohydrates and proteins. These tissues are to protect, absorb molecules or nutrients, and help sweep impurities away depending on the location in the body. Epithelial tissues protect the lining of the lungs, blood vessels, nose, mouth, and esophagus. Epithelial tissues lines kidney tubules, small intestines, and digestive tract.
 Work Cited
Work CitedMadder, Sylvia S. “Human Biology” 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2007
http://www.cramscience.ca/images/uploaded/uploadedLarge/1ff8e0a92c3974adacb557e5afa82bca.jpg (fats diagram)
http://www.ehrig-privat.de/ueg/images/dna-structure.jpg
(DNA diagram)
http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/cell1.gif
(animal/plant cell)
http://www.tnmanning.com/50d09290.jpg
(Prokaryotic cell)
http://webanatomy.net/histology/connective/areolar_proto.jpg
http://webanatomy.net/histology/connective/areolar_proto.jpg
(connective tissue)
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/8682.jpg
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/8682.jpg
(4 tissue types)
http://academic.wsc.edu/faculty/jatodd1/ap1/muscle.jpg
http://academic.wsc.edu/faculty/jatodd1/ap1/muscle.jpg
(neuron diagram)
http://www.biocam.com/images/wcepith2.jpg (epithelial tissue)
http://www.biocam.com/images/wcepith2.jpg (epithelial tissue)

No comments:
Post a Comment