Unit 2 Compendium Review # 1
-Cardiovascular system and Blood
-Cellular Respiration and oxygen
-Immunity and Microbes
-AIDS
Cardiovascular system and blood
The cardiovascular system consists of two major parts the heart and blood vessels. The heart its self has a major portion the myocardium that consists of cardiac muscle tissue and the pericardium a membranous sac that surrounds and protects the heart. Internally the heart consists of two sides the left and right, which the septum is what separates the heart into theses two sides. The heart is also broken down further into four chambers with two on the left side and two on the right. The upper two are called the right atrium and the left atrium, these are thin-walled atria. The lower two are thick-walled ventricles, called the left ventricle and the right ventricle. (picture of exterior heart anatomy)

The heart is a muscular organ that’s main purpose is to service the cells by pumping blood throughout the body. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs to be replenished with oxygen and then oxygen rich blood flows throw the heart to the left side to be pumped throughout the body. This pumping of the blood is called the heartbeat due to the contraction and relaxation of the heart. The internal heartbeat is regulated by the SA (senatorial) node which is located in the upper right atrium and is responsible for sending out an excitation impulse every .85 seconds that causes the atria to contract. When the atria is finished contracting and the excitation impulse reaches the AV(atrioventricular) node located in the lower right atrium near the septum the ventricles begin their contraction. This process is repeated every .85 seconds pumping blood through the body and making a heartbeat. The heart beat is also effected by external forces. First being a portion of the brain called the medulla oblongata is the cardiac control center that controls internal organs. The medulla oblongata changes the heartbeat by parasympathetic and sympathetic parts of the nervous system. Parasympathetic division decrease SA and VA nodal activity and sympathetic increases SA and VA nodal activity. SA and VA nodal activity are reduced when in a resting state and are increased when in an active state like exercising. Second the heartbeat is stimulated by the adrenal medulla by the releasing of hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine. So during exercise the heart beats stronger and faster due to sympathetic simulation and the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which pumps more blood to the body and cells.
The second major part of the cardiovascular system is the blood vessels. There are three types of blood vessels the arteries, capillaries and the veins. When the heart contracts and relaxes it is pumping blood through the lungs to be oxygenated and then through the body. The blood is carried through the body by these three blood vessels. The first being the arteries which are composed of three layers. The thin inner layer endothelium, the middle layer which is a fairly thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue and finally the outer layer that is connective tissue. (Picture of 3 tissue types)


(Picture showing blood flow from artery-capillaries-veins)

The main purpose of the circulation of blood is to service the cells. As the blood flows through the body it exchanges substances with tissue fluid which is the fluid that bathes cells. Blood removes waste from tissue fluid and replenishes the fluid with the oxygen and nutrients that cells need. After the blood performs this exchange it must get ride of the waste so that it can continue to perform this function for the cells. The blood is refreshed in the lungs, intestines, kidneys, and liver. The lungs remove carbon dioxide and replenishes the blood with oxygen. The kidneys clean the blood of waste collected from the cells. Nutrients enter the blood by the intestines while the liver removes amino acids and provides proteins. If any poisons entered at the intestines the liver removes them from the blood. Blood can perform these functions because it too is a tissue more precise a liquid tissue. Blood contains cells and cell fragments (formed elements) contained in a liquid called plasma. The formed elements in blood are red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
(Picture of red and white blood cells and platelets)

Red blood cells transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from cells and the lungs. Red blood cells lack a nucleus and most organelles like mitochondria but instead contain many copies of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is broken up into two parts the heme which contains an iron group that combines with O2 in the lungs and releases O2 in the tissues and the globin which is a protein containing four highly folded polypeptide chains. White blood cell are larger the red and there are less of them. They have a nucleus and lack hemoglobin. White blood cells fight infection and have various ways in which doing this. One being phagocytes, the cell surrounds the pathogen engulfing it and then enzymes from lysosome’s digest the pathogen. Another way is the production of antibodies that combine with foreign proteins and are marked for destruction. Platelets are pieces of large cells called megakaryocytic located in the red bone marrow. When blood vessels in the body are damage platelets clump together to act as a plug at the site of injury. If a large break occurs then blood clotting may be necessary to stop the bleeding. Red blood cells also get trapped in these clots making them appear red. Platelets and the damage tissue release prothrombin activator resulting in a fibrin threads that wind around the platelets holding the clot in place. As soon as the vessel in healed an enzyme destroys the fibrin network and the natural flow of plasma is restored.
(Picture of blood clot)

Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration occurs in the cells Mitochondrion an organelle in the cytoplasm. Mitochondrion coverts energy of glucose into chemical energy of ATP molecules. During this process mitochondria uses up oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. This process of cellular respiration of mitochondrion is very important to cellular metabolism. The blood is very important in this process because it’s the red blood cells that provide the oxygen and remove the carbon dioxide in the cells. As mentioned above after all the carbon dioxide has been switched out for oxygen the O2 deficient blood returns to the lungs to release the carbon dioxide in exchange for more O2 ,keeping the process repeating. (Picture of cellular respiration)
Immunity and Microbes
Microbes are microscopic organisms that can be found anywhere. They cover the surface of plants and animals they are even found on and within our own bodies. Many microbes are useful and apart of our daily lives. One type is bacteria that is a contributing factor in beer, cheese, bread, and drugs from biotechnology. Microbes that are decomposers are also very important to the cycle of life. Like anything else there are harmful bacteria and viruses called pathogens that cause diseases. (Picture of Microbes....#1Giardiasis, #2 Influenza, #3 Food poisoning, #4 Malaria, #5 Strep throat, #6 HIV/AIDS, #7 Tuberculosis, #8 Lyme disease, #9 Hepatitis B)
The body has nonspecific and specific defenses to protect the body. Nonspecific defensives are the skin, mucous membranes, chemical barriers, and resident bacteria. These are nonspecific because they do not discriminate since they block out all pathogens. The skin is a physical barrier that protects against invasion. Some barriers are the oil glands on skin, perspiration, saliva, and tears. These all contain antibacterial enzymes that prevent infections and/or wash away microbes. The last nonspecific defense resident bacteria is created by normal flora located in the mouth, intestines, and other areas of the body. Normal flora is very important and usefully and abusing antibiotics kills of normal flora make a person susceptible to pathogenic infections. The body is also protected by specific defenses. When pathogens get past nonspecific defenses and enter the body the immune system takes over. Antigens are the molecules that are foreign to the body such as bacteria and viruses. The immune system recognizes these antigens and fights them off. Memory B-cells produce antibodies that combine with like bacteria and kills it. Cytotoxic T-cells attack diseased cells by punching holes into the plasma membrane and injecting granzymes that cause the cell to die. And lastly helper T-cells controls and regulates immunity by secreting chemicals that gives orders to all types of immune cells. B-cells require the help of T cells to be activated. A person get vaccinations of common diseases because the body builds up an immunity to the disease by produce memory B-cells that kill that type of bacteria. Then if the bacteria gets into the body again the B-cells can destroy it. The vaccines are traditionally the disease itself or products that have been treated so that they no longer are able to cause the disease. This allows the body to make memory B-cells that are ready to fight off that disease if the body comes in contact with it in the future.
AIDS
AIDS is an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome that is caused by the HIV virus. When the body comes in contact with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) helper T-cells are destroyed inactivating the immune respone. As the number of helper T-cells are decline the more susceptible the body is to opportunistic infections. “An opportunistic infection Is one that has the opportunity to occur only because the immune system is severely weakened.”(mader pg 344) The most common way of acquiring HIV/AIDS is through sexual contact whether it be oral, vaginal, or anal intercourse. Other ways of receiving HIV/AIDS is breast milk, needle-sharing, or coming in contact with blood whether it’s a blood transfusion or a cut. There is no cure for AIDS instead there are treatments available to help slow down the spread of HIV in the cells. HAART highly active antiretroviral therapy is a combination of drugs designed to stop HIV from binding to receptors in the plasma membrane of uninfected cells. “Reverse transcriptase inhibitors, such as zidovudine (AZT), interfere with the operation of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. Integrase inhibitors prevent HIV from inserting its own genetic material into that of the host cells.”(madder pg350) This slows down the HIV virus and is commonly used during pregnancy to keep the baby from being infected with HIV. Once infected with HIV and the immune system is susceptible to infections it could take many years before they are AIDS positive or die. Many people die of AIDS related illnesses like Lymphoma, Kaposi Sarcomas, Tuberculosis and Pneumonia. A healthy immune system would be able to fight off most of these infections but since the HIV virus weakens the immune system you become susceptible. The young and the elderly are more susceptible than adults. Below are the latest statistics.
The latest statistics on the world epidemic of AIDS & HIV were published by UNAIDS/WHO in November 2006, and refer to the end of 2006.
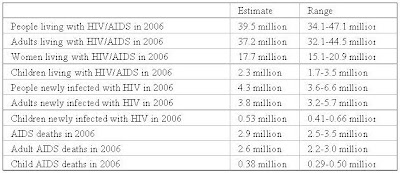
The number of people living with HIV has risen from around 8 million in 1990 to nearly 40 million today, and is still growing. Around 63% of people living with HIV are in sub-Saharan Africa.
Regional statistics for HIV & AIDS, end of 2006
* Proportion of adults aged 15-49 who were living with HIV/AIDS




No comments:
Post a Comment